Neck Zones for Cancer
When thinking of neck zones, there are those zones used in trauma and there are those used for cancer surgery.
The neck zones or levels depicted here are for cancer surgery. Lymph nodes or neck masses in these areas are described using these locations:
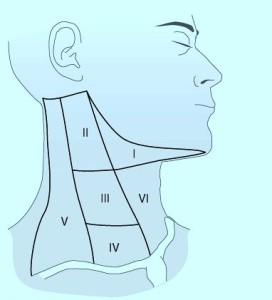
Picture copied from internet
- In patients presenting with solid neck masses – those masses associated with the thyroid move with swallowing. Those in levels 3,4, and 5 do not move with swallowing.
- Metastatic lymph nodes found in level 6 – could come from thyroid.
- U/S and FNA should be performed after exam/history for Solid Neck Mass.
- With well differentiated thyroid cancers, there is a high rate of cervical metastasis particularly with papillary cancers.
- With lateral lymph nodes involved in thyroid cancer, survival rate is not improved significantly with LN dissection in the neck for patients older than 60 years old or for men with a 4 cm or larger well differentiated cancer.
- Prophylactic lymph node dissections does not seem to improve survival with patients undergoing thyroid cancer treatment.
- If thyroid tumor is small with documented (U/S) lateral lymph nodes. There is a benefit to dissecting level 3 or 4 lymph nodes (lymph node dissection or modified dissection) in the younger patient.
Trauma neck zones
picture copied from internet: