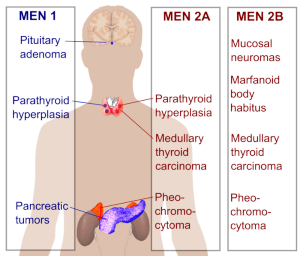
MEN syndromes
Inherited as autosomal dominant
All family members of a patient diagnosed with MEN syndromes should be screened for MEN.
Types: MEN I, MEN IIA, MEN IIB
MEN I
Most common tumors: mnemonic – PPP (all the P’s are followed by a vowel)
- Parathyroid hyperplasia (90% of patients have this)
- Pancreatic islet cell tumors (66%): Gastrinoma (ZE syndrome) 50%, Insulinoma 20%
- Pituitary tumors (66%)
Other tumors associated with MEN I = adenomas of Adrenal 30% and Thyroid 15%
MEN IIA
Most common tumors: mnemonic MPH – 2 miles per hour
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma 100%
- Pheochromocytoma 33%
- Hyperparathyroidism (50%), hypercalcemia
100% of patients with MEN IIA have medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.
MEN IIB
Most common abnormalities: mnemonic MMMP – 3M plastics
- Mucosal neuromas 100%
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma 85%
- Marfanoid
- Pheochromocytoma 50%
Physical findings of MEN IIB: Mucosal neuromas (mouth, eyes, etc), Marfanoid body shape, abnormal arch of foot, constipation.
Major difference between MEN IIA and IIB: MEN IIA has Hyperparathyroidism – hyperplasia, MEN IIB does not.
MEN I and MEN IIA have hyperplasia of the parathyroid – treated with removal of all parathyroid tissue with autotransplant of some parathyroid tissue – perhaps into the forearm.
Picture credit:
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/User:Mikael_H%C3%A4ggstr%C3%B6m